Mitosis
- in all body cells EXCEPT SEX CELLS
- for growth…repair…asexual reproduction
Meiosis
- in sex cells
- for sexual reproduction
Accuracy – How close a measurement is to the TRUE value
to increase accuracy, e.g. RE-ZERO a scale, read from a horizontal distance (avoid PARALLAX, position object at ZERO OF A RULER
Reliability – Repetitions
Precision – Decimal Places
Cambium immature cell (could become either a xylem or phloem cell)
| Tissue | Xylem | Phloem |
| Transport | Water an minerals from roots to shoots and leaves | Sucrose and amino acids produced in leaves during photosynthesis to every part of the plant |
| Process | Transpiration | Translocation |
| Structure | Cylindrical cells arranged end to end, in which the cytoplasm dies and the cell walls between adjoining cells breaks down leaving a dead empty tube with strengthened cell walls | Phloem tubes are made up of columns of living cylindrical cells. The cell walls between adjoining cells develop holes like a sieve allowing transport through the tube |
XYLEM VESSELS: Why does the water move up? What is the “transpiration stream”?
“Water is lost through the leaf of the plant by evaporation in a process called transpiration. This results in a pull on a column of water molecules which extends right down through the stem to the roots.
Water molecules are held together by hydrogen bonds. As a water molecule evaporates from the leaf, it pulls on the water molecule next to it, which in turn exerts a pull on the water molecule next to it and so on. This transmits a pull all the way down the column of water to the root system. In addition, the water molecules also adhere to the walls of the xylem vessel, preventing gravity from pulling the molecules back down.
So as each water molecule exits the leaf, it pulls the column of water molecules upwards from the root of the plant up the xylem and into the leaf. This upward movement of water resulting from the evaporation of water from the leaf is called the transpiration stream.” (from Pass My Exams)
24/10/13
Translocation
Sucrose is glucose molecules bonded together (in a condensation reaction). Sucrose can get broken down into glucose which is used for
*NOTE: Plants also need nitrates (absorbed from the soil as nitrate ions)
ALL THE STEPS ABOVE ARE NEEDED FOR MAX. MARKS IN EXAM QS. “NITRATES HELP PLANT GROW” IS REJECTED.
Sucrose is transported to:
Transpiration the evaporation of water at the surfaces of the mesophyll cells followed by loss of water vapour from plant leaves, through the stomata
Why are there more stomata on the bottom of the leaf?
General idea: MINIMISES WATER LOSS: THE PLANT DOES NOT WANT TO LOSE WATER.
The Nature and Variety of Living Organisms
Structures and Functions in Living Organisms
(f) Respiration
 (Experiments like this and variations)
(Experiments like this and variations)
(g) Gas exchange in humans
Transport in plants
1. Breathing the process of getting oxygen into the lungs and carbon dioxide out of the lungs
How are alveoli adapted for gas exchange?
| Feature | Function |
| Thin (one cell thick) | Short diffusion distance |
| Large surface area | Large volumes of gas can diffuse at once |
| Moist | Keeps cells alive |
| Well ventilated (constant fresh supplies of air) | Maintains concentration gradients for oxygen and carbon dioxide |
| Close to a blood supply | Efficient transport of gases to/from cells |
2. Respiration the process of releasing energy through the breakdown of glucose in all living cells
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| Requires oxygen | Does not require oxygen |
| Glucose + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H20 + 2900kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole of glucose) |
(In plants) Glucose -> carbon dioxide + ethanol + energy (In animals) Glucose -> lactic acid + energy |
| Produces a lot of energy | Does not produce a lot of energy |
| Involves mitochondria | Does not involve mitochondria |
Breathing and exercise
When we exercise…
…to deliver more oxygen and glucose to the muscles faster and remove carbon dioxide
Respiratory diseases
| Chemical | What it is | Long term effect on the body |
| Nicotine | Highly addictive drug |
|
| Tar |
|
|
| Carbon monoxide |
|
|
| Irritants and toxic substances |
|
|
Epithelium only one cell thick so that there is short distance for active transport and diffusion
Goblet cell produces mucus which protects gut lining against digestion by body’s own enzymes
Capillary transports glucose (from carbohydrate breakdown) and amino acids (from protein breakdown)
Lacteal transports fatty acids and glycerol (from fat breakdown)
Gland lined with cells which produce digestive enzymes including maltase
Vein delivers absorbed products to the liver via the hepatic portal vein
Artery delivers blood to villi
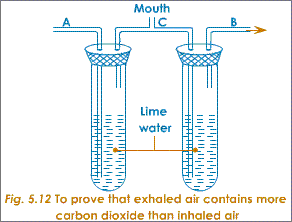
(A, B and C refer to the tubes unless specified)
Close end of B. Breathe in. Air from atmosphere enters through A, passes through limewater and enters your mouth (cannot enter through B because closed).
Open end of B and close end of A. Breathe out. Exhaled air passes through limewater in test tube B and exits through B.
Limewater in test tube B (which contained the air you exhaled) turns milky much faster than in test tube A (which contained the air you inhaled).