The Nature and Variety of Living Organisms
Structures and Functions in Living Organisms
- Preparation of plant and animal cells (onion and cheek cells for microscope observation)
- Osmosis in a model cell (Visking tubing – mass)
- Osmosis in potato cells (potatoes – length)
- Factors affecting the activity of catalase (raw/boiled/ground liver and hydrogen peroxide – height of froth)
- What temperature does amylase work best at? (starch suspension, water baths – color of iodine solution)
- Test for glucose (mixture of food extract and Benedict’s solution in boiling tube in hot water bath – blue -> yellow/red)
- Test for starch
- Measuring the energy values of foods (holding burning food under a boiling tube of water until food is fully burnt – temperature change)
(f) Respiration
- Respiration in animals and plants (breathing into a tube entering limewater)
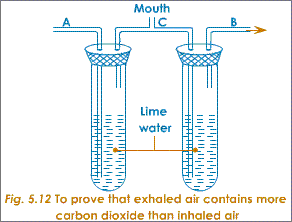 (Experiments like this and variations)
(Experiments like this and variations)
(g) Gas exchange in humans
- Effect of exercise on breathing rate http://www.curriculumonline.ie/en/Post-Primary_Curriculum/Senior_Cycle_Curriculum/Leaving_Certificate_Established/Biology/Biology_Support_Materials/Prescribed_Activities/Detailed_Templates/Investigate_the_effect_of_exercise_on_the_breathing_rate_or_pulse_rate_of_a_human.html
Transport in plants
- Role of environmental factors in determining the rate of transpiration from a leafy shoot
- effect of wind (distance of fan) – photometer setup
- effect of light (distance of lamp – put a layer of perspex in between) – photometer setup
- effect of humidity (different-sized plastic bags around leaves) – photometer setup